Internet Access Technologies
So, now you have a basic understanding of what makes up a network and the different types of networks. But, how do you actually connect users and organizations to the internet? As you may have guessed, there are many different ways to do this.
Home users, remote workers, and small offices typically require a connection to an ISP to access the internet. Connection options vary greatly between ISPs and geographical locations. However, popular choices include broadband cable, broadband digital subscriber line (DSL), wireless WANs, and mobile services.
Organizations usually need access to other corporate sites as well as the internet. Fast connections are required to support business services including IP phones, video conferencing, and data center storage. SPs offer business-class interconnections. Popular business-class services include business DSL, leased lines, and Metro Ethernet.
Home and Small Office Internet Connections
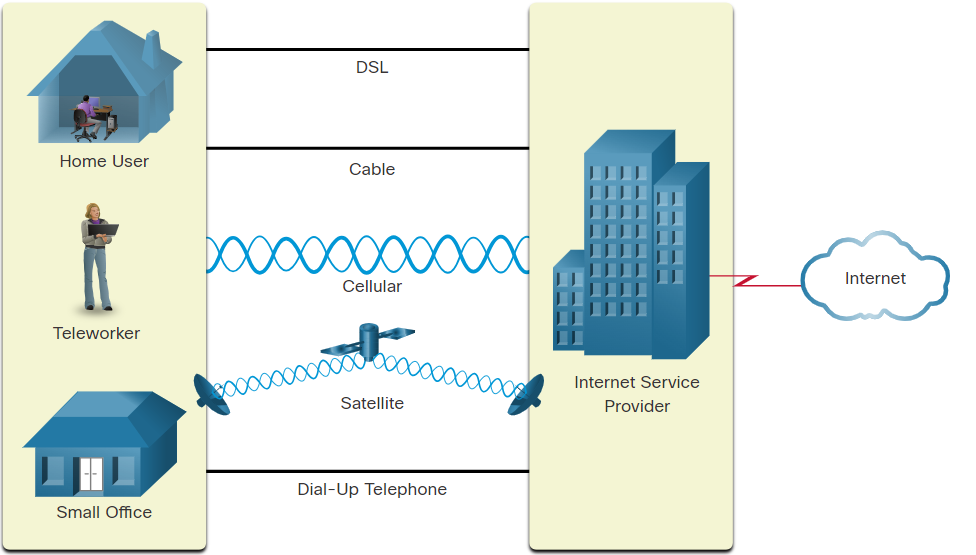
Cable- Typically offered by cable television service providers, the internet data signal transmits on the same cable that delivers cable television. It provides a high bandwidth, high availability, and an always-on connection to the internet.DSL- Digital Subscriber Lines also provide high bandwidth, high availability, and an always-on connection to the internet. DSL runs over a telephone line. In general, small office and home office users connect using Asymmetrical DSL (ADSL), which means that the download speed is faster than the upload speed.Cellular- Cellular internet access uses a cell phone network to connect. Wherever you can get a cellular signal, you can get cellular internet access. Performance is limited by the capabilities of the phone and the cell tower to which it is connected.Satellite- The availability of satellite internet access is a benefit in those areas that would otherwise have no internet connectivity at all. Satellite dishes require a clear line of sight to the satellite.Dial-up Telephone- An inexpensive option that uses any phone line and a modem. The low bandwidth provided by a dial-up modem connection is not sufficient for large data transfer, although it is useful for mobile access while traveling.
Businesses Internet Connections
Corporate connection options differ from home user options. Businesses may require higher bandwidth, dedicated bandwidth, and managed services. Connection options that are available differ depending on the type of service providers located nearby.
The figure illustrates common connection options for businesses.
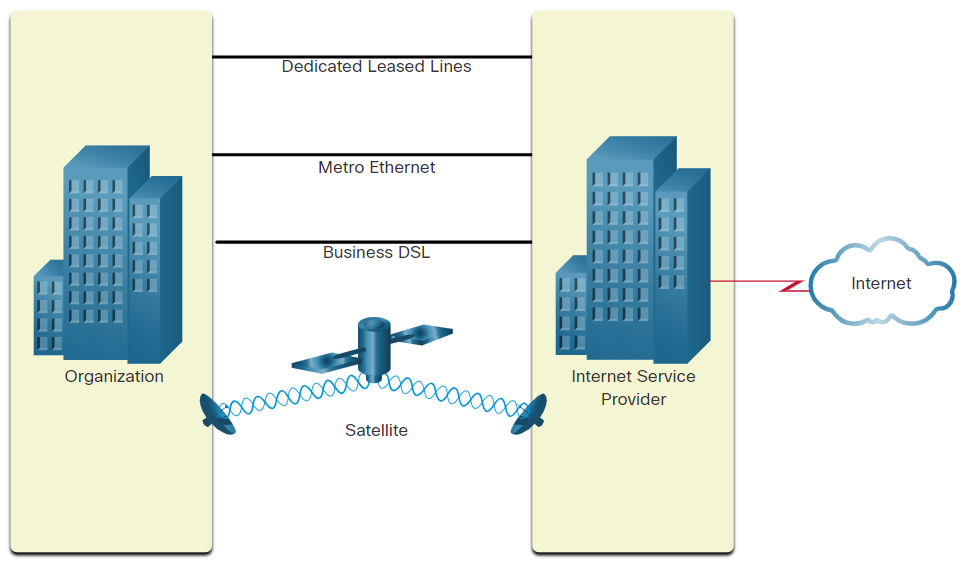
Dedicated Leased Line- Leased lines are reserved circuits within the service provider’s network that connect geographically separated offices for private voice and/or data networking. The circuits are rented at a monthly or yearly rate.Metro Ethernet- This is sometimes known as Ethernet WAN. In this module, we will refer to it as Metro Ethernet. Metro ethernets extend LAN access technology into the WAN. Ethernet is a LAN technology you will learn about in a later module.Business DSL- Business DSL is available in various formats. A popular choice is Symmetric Digital Subscriber Line (SDSL) which is similar to the consumer version of DSL but provides uploads and downloads at the same high speeds.Satellite- Satellite service can provide a connection when a wired solution is not available.
The Converging Network
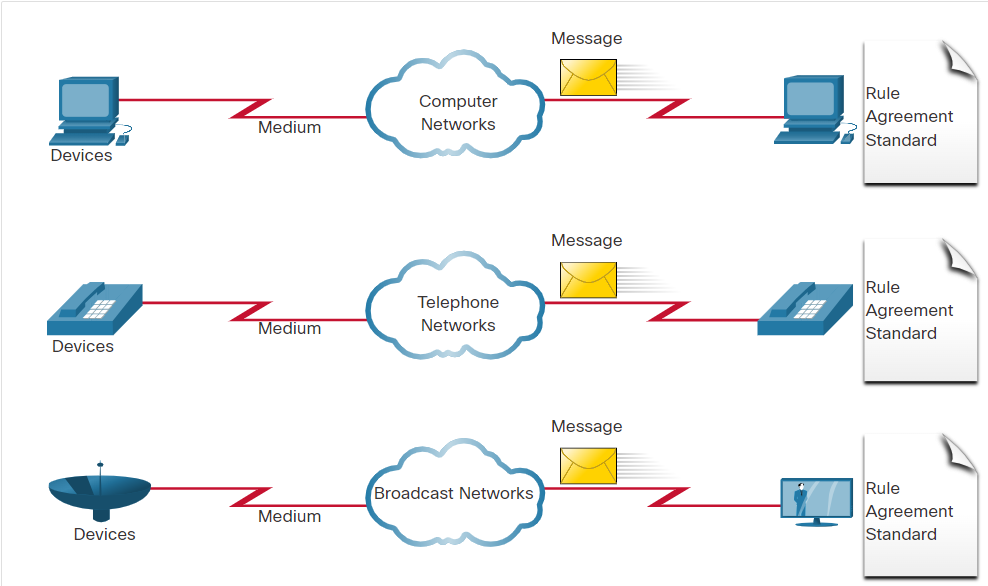
Traditional Separate Networks
Consider a school built thirty years ago. Back then, some classrooms were cabled for the data network, telephone network, and video network for televisions. These separate networks could not communicate with each other. Each network used different technologies to carry the communication signal. Each network had its own set of rules and standards to ensure successful communication. Multiple services ran on multiple networks.
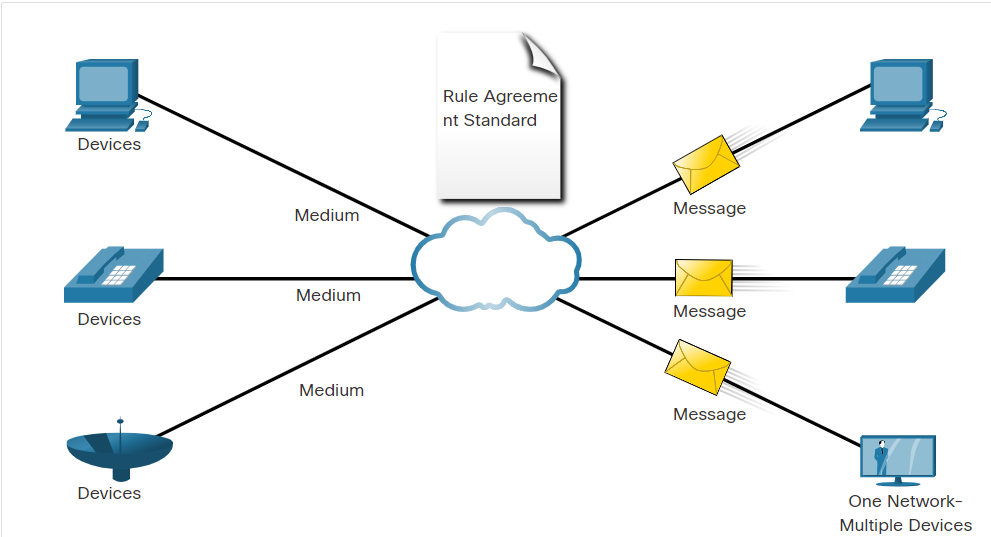
Converged Networks
Today, the separate data, telephone, and video networks converge. Unlike dedicated networks, converged networks are capable of delivering data, voice, and video between many different types of devices over the same network infrastructure. This network infrastructure uses the same set of rules, agreements, and implementation standards. Converged data networks carry multiple services on one network.
Packet Tracer - Network Representation
PKA File: Download