Azure Cloud Advocates at Microsoft are pleased to offer a 10-week, 20-lesson curriculum all about Data Science. Each lesson includes pre-lesson and post-lesson quizzes, written instructions to complete the lesson, a solution, and an assignment. Our project-based pedagogy allows you to learn while building, a proven way for new skills to ‘stick’.
This website content is from Microsoft Github Repo: Data-Science-For-Beginners
All the content in this site is stripped down from the original repo and I only copy the relevant info for me to this site.
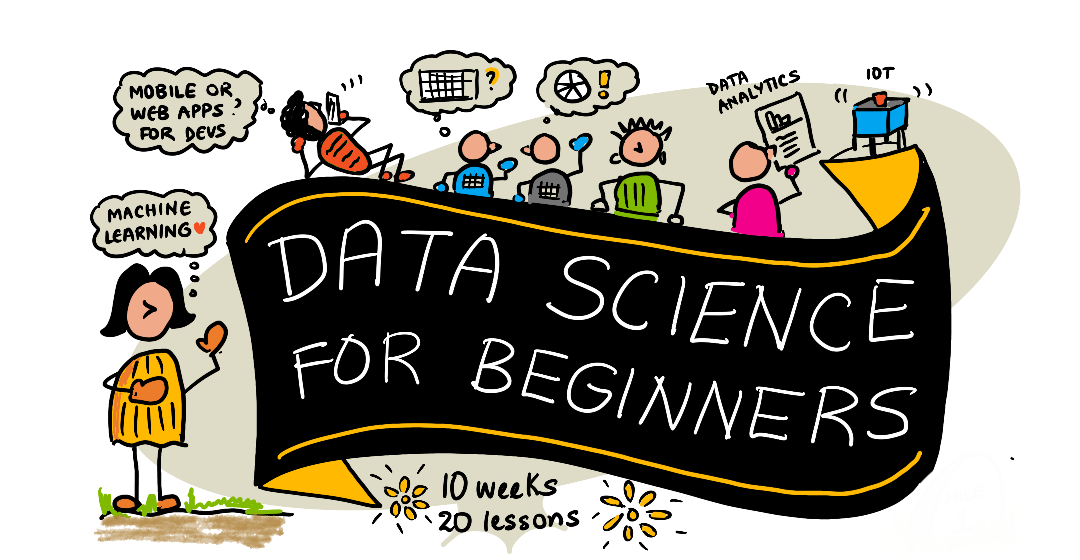 |
|---|
| Data Science For Beginners - Sketchnote by @nitya |
Are you a student?
Get started with the following resources:
- Student Hub page In this page, you will find beginner resources, Student packs and even ways to get a free cert voucher. This is one page you want to bookmark and check from time to time as we switch out content at least monthly.
- Microsoft Learn Student Ambassadors Join a global community of student ambassadors, this could be your way into Microsoft
Getting Started
Students: to use this curriculum on your own, fork the entire repo and complete the exercises on your own, starting with a pre-lecture quiz. Then read the lecture and complete the rest of the activities. Try to create the projects by comprehending the lessons rather than copying the solution code; however, that code is available in the /solutions folders in each project-oriented lesson. Another idea would be to form a study group with friends and go through the content together. For further study, we recommend Microsoft Learn.
Meet the Team
Pedagogy
We have chosen two pedagogical tenets while building this curriculum: ensuring that it is project-based and that it includes frequent quizzes. By the end of this series, students will have learned basic principles of data science, including ethical concepts, data preparation, different ways of working with data, data visualization, data analysis, real-world use cases of data science, and more.
In addition, a low-stakes quiz before a class sets the intention of the student towards learning a topic, while a second quiz after class ensures further retention. This curriculum was designed to be flexible and fun and can be taken in whole or in part. The projects start small and become increasingly complex by the end of the 10 week cycle.
Each lesson includes:
- Optional sketchnote
- Optional supplemental video
- Pre-lesson warmup quiz
- Written lesson
- For project-based lessons, step-by-step guides on how to build the project
- Knowledge checks
- A challenge
- Supplemental reading
- Assignment
- Post-lesson quiz
A note about quizzes: All quizzes are contained in this app, for 40 total quizzes of three questions each. They are linked from within the lessons, but the quiz app can be run locally; follow the instruction in the quiz-app folder. They are gradually being localized.
Lessons
 |
|---|
| Data Science For Beginners: Roadmap - Sketchnote by @nitya |
Introduction
| Lesson Number | Topic | Learning Objectives | Linked Lesson | Author |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | Defining Data Science | Learn the basic concepts behind data science and how it’s related to artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data. | lesson video | Dmitry |
| 02 | Data Science Ethics | Data Ethics Concepts, Challenges & Frameworks. | lesson | Nitya |
| 03 | Defining Data | How data is classified and its common sources. | lesson | Jasmine |
| 04 | Introduction to Statistics & Probability | The mathematical techniques of probability and statistics to understand data. | lesson video | Dmitry |
Working with Data
| Lesson Number | Topic | Learning Objectives | Linked Lesson | Author |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 05 | Working with Relational Data | Introduction to relational data and the basics of exploring and analyzing relational data with the Structured Query Language, also known as SQL (pronounced “see-quell”). | lesson | Christopher |
| 06 | Working with NoSQL Data | Introduction to non-relational data, its various types and the basics of exploring and analyzing document databases. | lesson | Jasmine |
| 07 | Working with Python | Basics of using Python for data exploration with libraries such as Pandas. Foundational understanding of Python programming is recommended. | lesson video | Dmitry |
| 08 | Data Preparation | Topics on data techniques for cleaning and transforming the data to handle challenges of missing, inaccurate, or incomplete data. | lesson | Jasmine |
Data Visualization
| Lesson Number | Topic | Learning Objectives | Linked Lesson | Author |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 09 | Visualizing Quantities | Learn how to use Matplotlib to visualize bird data 🦆 | lesson | Jen |
| 10 | Visualizing Distributions of Data | Visualizing observations and trends within an interval. | lesson | Jen |
| 11 | Visualizing Proportions | Visualizing discrete and grouped percentages. | lesson | Jen |
| 12 | Visualizing Relationships | Visualizing connections and correlations between sets of data and their variables. | lesson | Jen |
| 13 | Meaningful Visualizations | Techniques and guidance for making your visualizations valuable for effective problem solving and insights. | lesson | Jen |
Data Science Lifecycle
| Lesson Number | Topic | Learning Objectives | Linked Lesson | Author |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | Introduction to the Data Science lifecycle | Introduction to the data science lifecycle and its first step of acquiring and extracting data. | lesson | Jasmine |
| 15 | Analyzing | This phase of the data science lifecycle focuses on techniques to analyze data. | lesson | Jasmine |
| 16 | Communication | This phase of the data science lifecycle focuses on presenting the insights from the data in a way that makes it easier for decision makers to understand. | lesson | Jalen |
Data Science in the Cloud
| Lesson Number | Topic | Learning Objectives | Linked Lesson | Author |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17 | Data Science in the Cloud | This series of lessons introduces data science in the cloud and its benefits. | lesson | Tiffany and Maud |
| 18 | Data Science in the Cloud | Training models using Low Code tools. | lesson | Tiffany and Maud |
| 19 | Data Science in the Cloud | Deploying models with Azure Machine Learning Studio. | lesson | Tiffany and Maud |
Data Science in the Wild
| Lesson Number | Topic | Learning Objectives | Linked Lesson | Author |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | Data Science in the Wild | Data science driven projects in the real world. | lesson | Nitya |
GitHub Codespaces
Follow these steps to open this sample in a Codespace:
- Click the Code drop-down menu and select the Open with Codespaces option.
- Select + New codespace at the bottom on the pane. For more info, check out the GitHub documentation.
VSCode Remote - Containers
Follow these steps to open this repo in a container using your local machine and VSCode using the VS Code Remote - Containers extension:
- If this is your first time using a development container, please ensure your system meets the pre-reqs (i.e. have Docker installed) in the getting started documentation.
To use this repository, you can either open the repository in an isolated Docker volume:
Note: Under the hood, this will use the Remote-Containers: Clone Repository in Container Volume… command to clone the source code in a Docker volume instead of the local filesystem. Volumes are the preferred mechanism for persisting container data.
Or open a locally cloned or downloaded version of the repository:
- Clone this repository to your local filesystem.
- Press F1 and select the Remote-Containers: Open Folder in Container… command.
- Select the cloned copy of this folder, wait for the container to start, and try things out.
Offline access
You can run this documentation offline by using Docsify. Fork this repo, install Docsify on your local machine, then in the root folder of this repo, type docsify serve. The website will be served on port 3000 on your localhost: localhost:3000.
Note, notebooks will not be rendered via Docsify, so when you need to run a notebook, do that separately in VS Code running a Python kernel.